Recently I was chatting with some friends about the 2015 study that “proved” squirting is the same thing as peeing, and I got incensed afresh about it. You can read the study yourself online if you’re curious, though I’m about to make the case for why you probably shouldn’t.
To be perfectly clear: I am not a scientist, nor am I a doctor. I have, however, been a sex journalist for nearly a decade, so I’m pretty accustomed to reading studies and extracting key findings from them. I first became interested in this study when I wrote a piece about it for Maisonneuve years ago, and I interviewed many experts and key players in the field as part of that project. With all of that said, here are 8 reasons this study is, in my view, not to be trusted…
1. It only had seven (7) participants. SEVEN. Many experts agree that studies smaller than about 100 people are unlikely to be statistically significant or predictive of a general population. I asked the lead researcher, Samuel Salama, why he only studied seven women, and he said, “I wish [I had] more, but it is difficult to recruit women who accept to participate to the protocol [sic].” He also claimed that his study was nonetheless the largest one that had been done on the topic, which is in fact false; previous studies done on the squirting-versus-pee debate have included sample sizes as large as 27, and there was even a previous biochemical analysis study on this subject that had 11 participants. (Still not enough, but better than seven, I guess.)
In an interview, I asked a sexual health research coordinator what they thought about this study only having seven participants, and they said this:
“I think, if you only study seven people, that’s just ridiculous. Like, what the fuck. That is not statistically significant in any universe. It doesn’t prove anything. … It’s bonkers! Bonkers! Seven people is like, nothing.”
2. The lead researcher seems to have had an axe to grind. I asked lead researcher Samuel Salama why he decided to study this topic, and he told me it was his 3rd-year sexology thesis and that he chose the subject of squirting “because you can read a lot of bullshit on the topic.” This suggests to me that he had already formed an opinion about whether squirting is pee before he even began the study, since he felt all the previous research on it was “bullshit.” Scientists are supposed to keep an open mind about the potential results of their studies; otherwise, the results are prone to being tainted, just like Salama thinks ejaculate is tainted by pee.
3. Participants were recruited under odd circumstances. The study’s seven participants were all referred by physicians, which suggests to me that the women themselves, their doctors, and the study creators all viewed squirting as a medical issue rather than a normal part of sexual functioning. This creates a biased dynamic that no doubt would permeate the whole study. Participants were also required to have a BMI that falls within the “healthy” range despite BMI having been long ago debunked as a useful measure of body weight and health.
In an interview, I asked a postdoctoral research fellow at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health if it could be problematic that all the participants were recruited via their physicians, and she said this:
“It definitely creates limitations on the generalizability of the results. For example, since the sample is limited to a certain set of women who saw these particular physicians and were then referred, we have to consider whether or not there are systematic differences between a) women who choose and/or are able to visit a physician and those who do not or cannot, b) the characteristics of women who visited the specific physicians included in the study versus women who selected different physicians, or c) women who were referred to the study and actually participated, versus women who were referred and chose not to participate, to name a few issues. Thus, the interpretation of the results should be considered within these limitations.”
4. It’s cissexist. I mean, it’s certainly not unique among sexological studies in this way, unfortunately, but this is still worth pointing out. So-called “female ejaculation” is a phenomenon that can happen to anyone who has a vagina, not just cis women.
5. It took place in a lab setting. This, again, is definitely not unique among sex studies, but I do think it’s worth noting because we just don’t have the same sexual responses in cold, clinical environments as we would have in our own cozy beds. IMO it’s absurd to think that someone getting sexually stimulated in a lab room, while being monitored and measured, would have exactly the same experience of and response to that stimulation as she has at home. As Emily Nagoski, Ph.D., details in her book Come As You Are, stress has a physiologically inhibiting effect on sexual arousal, and thus I don’t think a sex study can be purely effective and accurate in a lab setting. The participants of this study even noted that the amount they squirted during the study was less than they tend to squirt at home, suggesting the results were in fact different than they would be in everyday life.
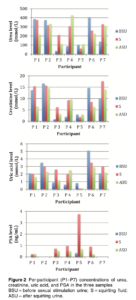 6. The results were inconclusive, but not described as such in the study. This, to me, is the most pressing and obvious reason this study is problematic. The study measured levels of urea, creatinine, uric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in each participant’s pee both before sex and after sex, and also measured those levels in each participant’s squirt. Those first three ingredients – urea, creatinine, and uric acid – are found in urine, while PSA is typically not.
6. The results were inconclusive, but not described as such in the study. This, to me, is the most pressing and obvious reason this study is problematic. The study measured levels of urea, creatinine, uric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in each participant’s pee both before sex and after sex, and also measured those levels in each participant’s squirt. Those first three ingredients – urea, creatinine, and uric acid – are found in urine, while PSA is typically not.
If you look at the graphs that lay out the data on what was actually in each sample (click the image to see it larger), you’ll see that the distribution is actually pretty all-over-the-place. Some participants’ squirt (represented by the red bar in each chart) contained medium-to-high levels of the components of urine, while some contained barely any at all. Most participants’ squirt contained a high proportion of prostate-specific antigen compared to other ingredients, which – if anything – supports the idea that squirt is a separate fluid from urine, containing its own unique ingredients.
The writers of the study note early on, “Because normality of data distribution could not be ascertained, we preferred to use the median as the measure of central tendency and minimum–maximum values as the measure of variability.” This is just not a fair or effective way to do a study like this. Even I, as a relative layperson, can glance at these results and see that some of the women’s squirt is scientifically similar to their pee, and some of the women (especially participant #5, and to a lesser extent, #4 and #6) clearly squirt a liquid that is demonstrably different from their urine. You can’t just “average out” the results and decide that a handful of women squirting something chemically similar to pee means all women who ever squirt are squirting pee – especially when the results of your own study don’t even bear that out!
7. There’s traces of pee in penile ejaculate, too. It is well-established that semen contains uric acid and urea, probably due to the fact that both urine and semen come from the same hole and will naturally intermingle to some extent. I would argue (as did many of my scientist interviewees) that the same happens for people with vulvas, and that this explains the overlap in chemical makeup between some vulva-possessing people’s urine and ejaculate.
And finally… 8. This study will damage, and has damaged, the lives of people who squirt. The hypothesis that squirting = pee has already caused so much pain, stigma, and even trauma in the world. I interviewed Spanish sex educator Diana J. Torres about squirting and they told me stories of women they’ve known who have had their G-spots surgically removed as treatment for “coital incontinence” that was actually just squirting. “Usually science is not separated from politics,” they said, “and in a patriarchal system, it has been instrumentalized to support it.” I have to agree.
In the aftermath of this study being published, headlines circulated worldwide, announcing that squirt was actually just pee. My friend Epiphora launched a “#NotPee” campaign on social media to fight against the stigma and misinformation. Many people replied to say that they’d been shamed for squirting in the past. I hate to think what happens when that shaming escalates to ostracization or even violence.
“I don’t know why they keep revisiting it. I don’t know what the political import is to prove that it’s urine. It seems weird to me,” said philosophy professor (and proud squirter) Shannon Bell when I interviewed her about this. “If you compare it to studies on [penile] ejaculate, there’s almost an investment in women’s ejaculate not being as sexual a fluid… and I would say that’s got a political component to it.” Like Bell, I see this entire debate as being yet another manifestation of the male-dominated science field refusing to believe women and other people of marginalized genders about their own damn bodies.
I’m tired of it. I want better, bigger studies on the subject, that are constructed in more compassionate and sensical ways. But mostly, I just want people to stop caring so much whether squirt is pee and whether pee is gross. There is a lot about sex that could be considered gross, and most of us continue to have it anyway. If you’re actually disgusted by your partner’s pleasure, maybe you should let them go so they can find a partner who actually wants them to have a good time in bed without feeling ashamed of their body and the fluids it produces.